活动类别:网络信息安全系列学术报告
活动时间:15:00-17:30
活动日期:2019-06-29
地点:长安校区 文津楼三段6层628报告厅
主办单位:best365在线官网登录入口 网络信息安全团队
活动日程安排:
报告题目一:Automated forensic analysis of mobile applications on Android devices
报告时间:15:00-16:15
报告人:Xiaodong Lin, Associate Professor
报告内容简介
It is not uncommon that mobile phones are involved in criminal activities, e.g., the surreptitious collection of credit card information. Forensic analysis of mobile applications plays a crucial part in order to gather evidences against criminals. However, traditional forensic approaches, which are based on manual investigation, are not scalable to the large number of mobile applications. On the other hand, dynamic analysis is hard to automate due to the burden of setting up the proper runtime environment to accommodate OS differences and dependent libraries and activate all feasible program paths. In this talk, we introduce a fully automated tool, Fordroid for the forensic analysis of mobile applications on Android. Fordroid conducts inter-component static analysis on Android APKs and builds control flow and data dependency graphs. Furthermore, Fordroid identifies what and where information written in local storage with taint analysis. Data is located by traversing the graphs. This addresses several technique challenges, which include inter-component string propagation, string operations (e.g., append) and API invocations. Also, Fordroid identifies how the information is stored by parsing SQL commands, i.e., the structure of database tables. Finally, we selected 100 random Android applications consisting of 2841 components from four categories for evaluation. Analysis of all apps took 64 h. Fordroid discovered 469 paths in 36 applications that wrote sensitive information (e.g., GPS) to local storage. Furthermore, Fordroid successfully located where the information was written for 458 (98%) paths and identified the structure of all (22) database tables.
报告人简介
Xiaodong Lin received the PhD degree in Information Engineering from Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China, and the PhD degree (with Outstanding Achievement in Graduate Studies Award) in Electrical and Computer Engineering from the University of Waterloo, Canada. He is currently an Associate Professor in the School of Computer Science at the University of Guelph, Canada. His research interests include wireless communications and network security, computer forensics, software security, and applied cryptography. Dr. Lin serves as an Associate Editor for many international journals. He has served or is serving as a guest editor for many special issues of IEEE, Elsevier and Springer journals and as a symposium chair or track chair for IEEE/ACM conferences. He also served on many program committees. He was Chair of Communications and Information Security Technical Committee (CISTC) – IEEE Communications Society (2016-2017). He is a Fellow of the IEEE.
报告题目二:Efficient Privacy-Preserving Data Merging and Skyline Computation over Multi-Source Encrypted Data
报告时间:16:15-17:30
报告人:Rongxing Lu Assistant Professor
报告内容简介
Efficient data merging from the significant amount of data routinely collected from various data sources is crucial in the uncovering of relevant and key information of interest (e.g. skyline). There are, however, privacy considerations during data merging and skyline operations, particularly when dealing with sensitive data (e.g., healthcare data). Existing focuses on data merging and skyline computation either do not (fully) consider data privacy or have low efficiency. Thus, in this talk, we aim to address both privacy and efficiency during data merging and skyline computations over multi-source encrypted data. Specifically, we integrate the leftist tree with public key encryption and index based skyline computation to achieve data merging and skyline computation over encrypted data. Specifically, we first design a non-interactive data comparison protocol using public key encryption technique. This allows us to compare encrypted and outsourced data under a single cloud server instead of two non-colluding cloud servers in previous studies. Then, we combine the leftist tree with public key encryption to achieve privacy-preserving data merging with high efficiency, namely, 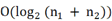 computational complexity for merging two leftist trees of sizes
computational complexity for merging two leftist trees of sizes 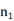 and
and 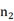 . Third, we present an index and leftist tree based skyline computation algorithm, which can efficiently perform skyline query over the merged encrypted data. Then, detailed security analysis and performance evaluation demonstrate that our scheme is both secure and efficient for data merging and skyline computation.
. Third, we present an index and leftist tree based skyline computation algorithm, which can efficiently perform skyline query over the merged encrypted data. Then, detailed security analysis and performance evaluation demonstrate that our scheme is both secure and efficient for data merging and skyline computation.
报告人简介
Rongxing Lu (S’99-M’11-SM’15) has been an assistant professor (promoted to associate professor on July 1, 2019) at the Faculty of Computer Science (FCS), University of New Brunswick (UNB), Canada, since August 2016. Before that, he worked as an assistant professor at the School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore from April 2013 to August 2016. Rongxing Lu worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow at the University of Waterloo from May 2012 to April 2013. He was awarded the most prestigious “Governor General’s Gold Medal”, when he received his PhD degree from the Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo, Canada, in 2012; and won the 8th IEEE Communications Society (ComSoc) Asia Pacific (AP) Outstanding Young Researcher Award, in 2013. He is presently a senior member of IEEE Communications Society. His research interests include applied cryptography, privacy enhancing technologies, and IoT-Big Data security and privacy. He has published extensively in his areas of expertise, and was the recipient of 8 best (student) paper awards from some reputable journals and conferences. Currently, Dr. Lu currently serves as the Vice-Chair (Publication) of IEEE ComSoc CIS-TC (Communications and Information Security Technical Committee). Dr. Lu is the Winner of 2016-17 Excellence in Teaching Award, FCS, UNB.